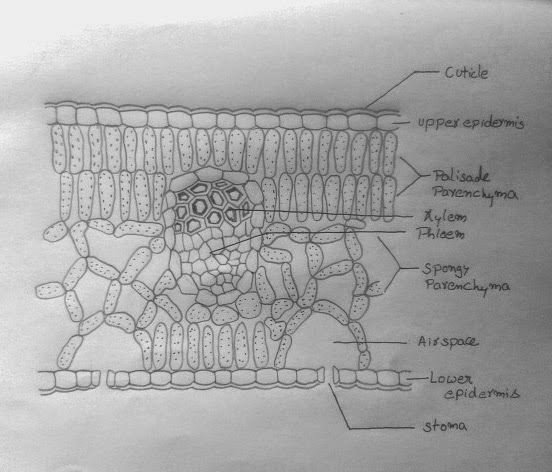
A transverse section of a typical leaf shows that it is covered by epidermis on both surfaces the upper epidermis on the upper surface and lower epidermis on the lower surface. Lower epidermis is interrupted by a large number of opening called stomata. The central opening is called stoma. Each stoma is surrounded by the two kidney-shaped cells called Guard cells. Stomata regulate the exchange of gases and loss of water vapor from the leaves.Tissue enclosed between the two epidermal layers is called the Mesophyll. Mesophyll consists of elongated cells arranged in rows called the Palisade parenchyma. It also has irregularly arranged cells with large intercellular spaces known as spongy parenchyma. The mesophyll cells contain abundant chloroplasts. More palisade tissue occur in leaves exposed to bright light than those exposed to shade. Vascular bundles in the leaf are located in the midrib and the veins. In each vascular bundle of the leaf, phloem is located towards the lower side and xylem toward the upper side.
Now let`s start the diagram-
Step 1:
Draw two faint parallel line as shown.
Draw outlines of central vascular bundle
and air spaces above stomata.
Step2:
Erase the faint lines and draw wavy patter of
epidermis as shown.
Step3:
Complete the wavy pattern on both sides of the
diagram as shown. Note that the edges of outer line should face the edge of inner line exactly.
Step 4:
Connect the edges of the lines to create barrel shaped epidermal cells on both sides.
Complete the bundle sheath cells of vascular bundle too by same technique.
Step 5:
Draw cuticle on both epidermis following the contours of the epidermal cell.
Step 6:
Draw the mesophyll cells lining the air spaces as shown.
Draw palisade tissue as shown along the upper epidermis.
Step 7:
Complete drawing the palisade tissue as shown.
Draw spongy tissue as shown.
Put several dots in all mesophyll cell which represent chloroplasts.
If your leaf specimen has trichomes you can draw on upper epidermis.
Step 8:
Draw hexagonal cells in vascular bundle in top position as shown. Do not leave any spaces between these cells.
Draw thick cell walls inside xylem with thick lines use little pressure.
Step 9:
Complete phloem as shown with several small hexagonal cells.
Label the diagram neatly as shown.
Continuation:- Leaf anatomy is suitable for entry of carbon dioxide into the closely packed palisade cells of the leaf. More photosynthetic activity takes place in the upper side of the leaf. On this side, the palisade cells contain more number of chloroplasts than the loosely arranged spongy parenchyma cells towards inner side. Organization of the leaf is suitable for entry of raw materials, synthesis of sugar and transport of the photosynthate. Gaseous carbon dioxide passes from atmosphere into the leaf through diffusion and reaches the chloroplasts. Water is transported from the roots through xylem by veins and its branches called veinlets. There is a large surface area to receive light on leaf lamina. Oxygen produced during photosynthesis diffuses outside through stomata. Sugar is converted into starch in the chloroplast during the day time and starch is to sugar. This sugar will pass through phloem to other parts of the plant.











7 comments:
Great effort :D
thx it every helpful
Thanks a lot! It helped me get full marks in the last minute!!!
Bravo!!
Superb!!
Nice one💖
great work ..
omgggggg
Post a Comment